Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
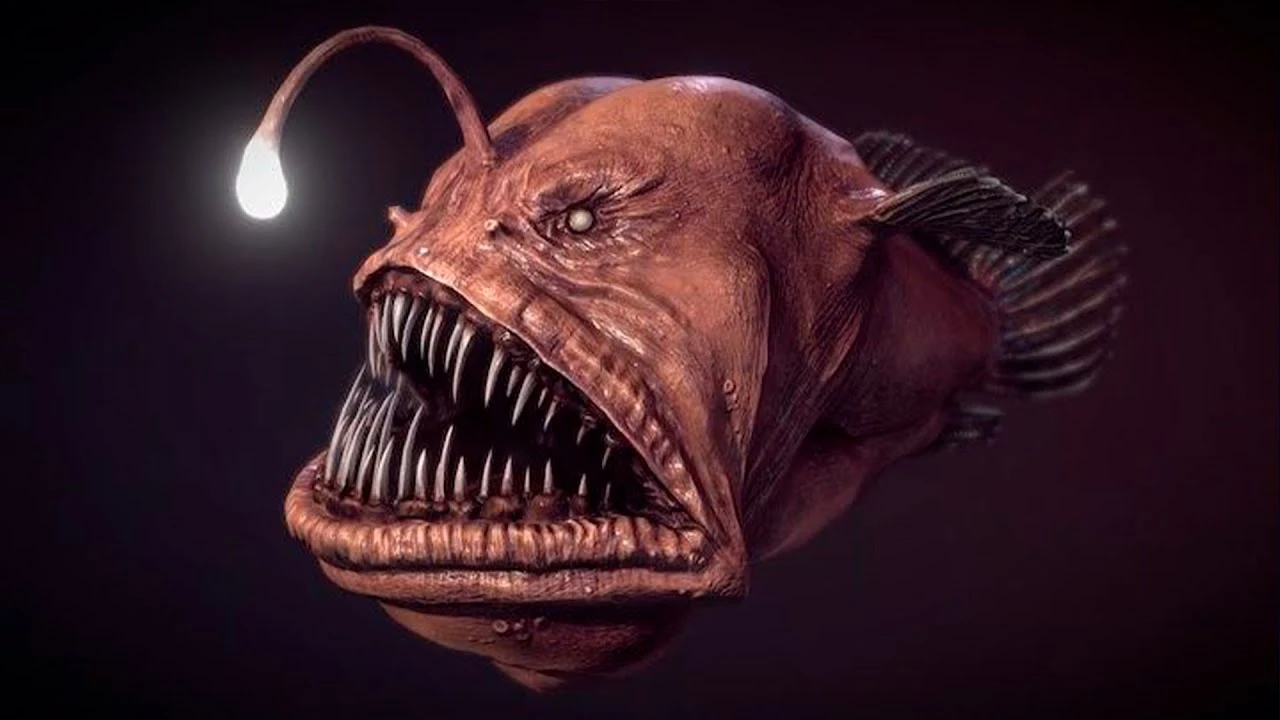

In the vast, pitch-black depths of the ocean, where sunlight never reaches, the anglerfish reigns as one of the most mysterious and fascinating creatures. Known for its terrifying appearance and unique adaptations, this deep-sea dweller has intrigued scientists and captivated the imagination of many. This article delves into the world of the anglerfish, exploring its extraordinary adaptations, the eerie beauty of its bioluminescence, and the survival strategies that make it a true marvel of the deep ocean.
The anglerfish belongs to the order Lophiiformes, a diverse group of fish known for their unique predatory techniques and adaptations to deep-sea life. Within this order, there are several families, but the most famous and widely recognized anglerfish are part of the family Ceratiidae, also known as the sea devils. This family is characterized by their globular bodies, large mouths, and the distinctive bioluminescent lure that dangles from their heads.
Anglerfish species vary greatly in size, appearance, and habitat, but they all share the common trait of the bioluminescent lure. While many anglerfish species are found in the deep ocean, some species inhabit shallower coastal waters. The diversity within this group is a testament to the anglerfish’s remarkable evolutionary success in adapting to a range of marine environments.
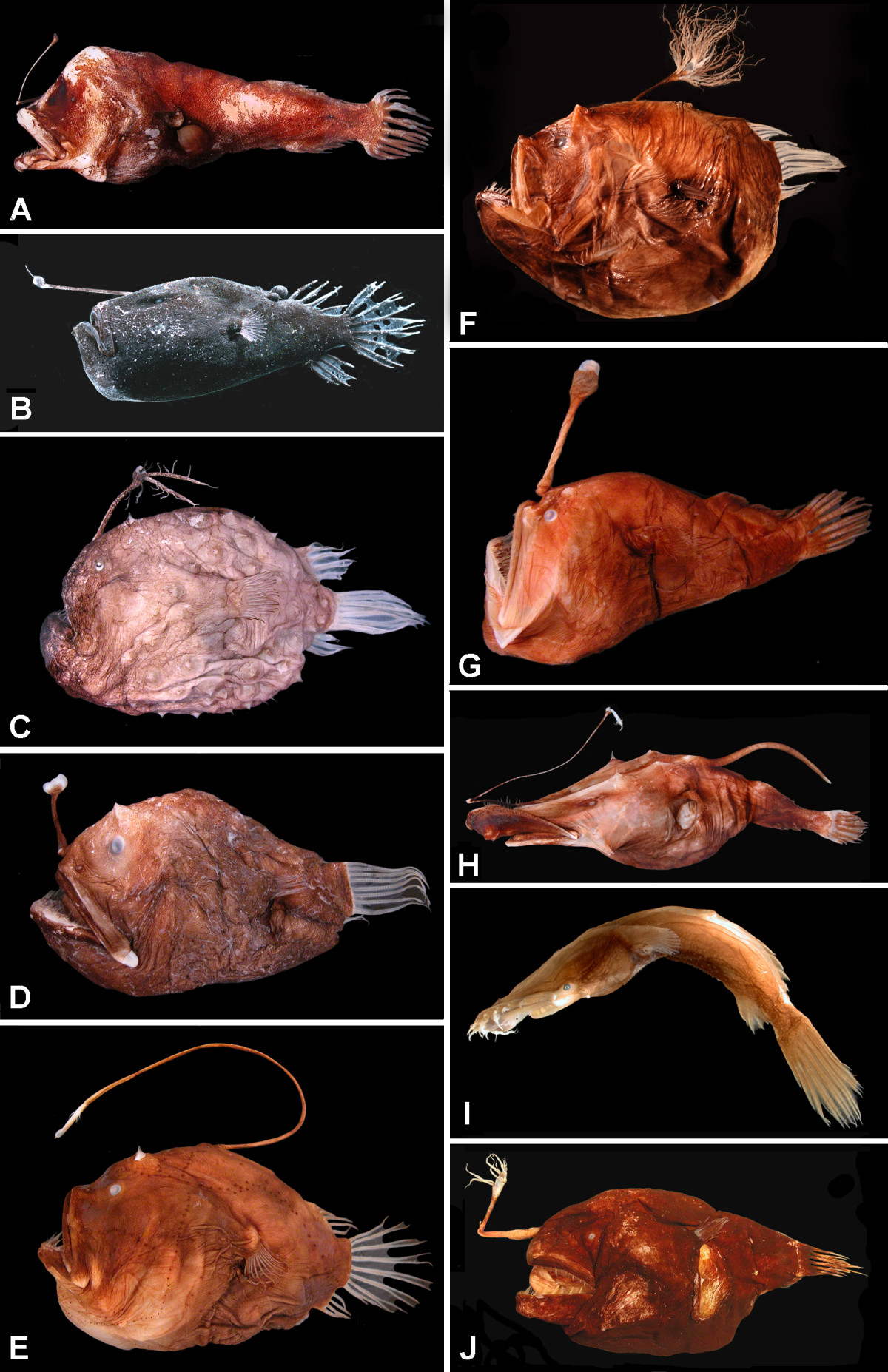
(A) Centrophryne spinulosa, 136 mm SL
(B) Cryptopsaras couesii, 34.5 mm SL
(C) Himantolophus appelii, 124 mm SL
(D) Diceratias trilobus, 86 mm SL
(E) Bufoceratias wedli, 96 mm SL
(F) Bufoceratias shaoi, 101 mm SL
(G) Melanocetus eustalus, 93 mm SL
(H) Lasiognathus amphirhamphus, 157 mm SL
(I) Thaumatichthys binghami, 83 mm SL
(J) Chaenophryne quasiramifera, 157 mm SL.
One of the most striking features of the anglerfish is its bioluminescent lure, a glowing appendage that extends from its head. This light-producing organ, known as the esca, is not just for show—it serves a deadly purpose. In the inky darkness of the deep sea, where food is scarce, the anglerfish uses its bioluminescence to attract unsuspecting prey. Small fish, squid, and other creatures are drawn to the light, mistaking it for a safe haven. Little do they know, they are swimming straight into the jaws of the anglerfish.
(Skeleton of the anglerfish Lophius piscatorius: The first spine of the dorsal fin of the anglerfish acts as a fishing rod with a lure.)
The bioluminescence is produced by symbiotic bacteria living within the esca. These bacteria emit light through a chemical reaction, a phenomenon that has evolved to perfection in the anglerfish. The ability to produce light in complete darkness not only aids in hunting but also in communication and mating, making bioluminescence a critical survival tool in the deep sea.
The deep-sea environment is one of the most extreme habitats on Earth, characterized by crushing pressures, freezing temperatures, and complete darkness. The anglerfish has evolved a range of adaptations that allow it to thrive in these harsh conditions.
One of the most remarkable adaptations is its highly flexible jaw and expandable stomach. The anglerfish can consume prey up to twice its own size, a necessary adaptation in a habitat where meals are few and far between. Its sharp, fang-like teeth curve inward, ensuring that once prey is caught, escape is impossible.
Moreover, the anglerfish’s body is adapted to withstand the immense pressure of the deep sea. Unlike most fish, which would be crushed under such pressure, the anglerfish has a soft, gelatinous body that allows it to survive where few others can.
Perhaps one of the most bizarre aspects of the anglerfish is its reproductive strategy. In many species of anglerfish, males are significantly smaller than females. The male’s primary role in life is to find a mate in the vast expanse of the deep sea—a task made easier by the female’s bioluminescent lure.
Once a male finds a female, he bites into her skin and fuses with her body. Over time, the male becomes little more than a parasitic appendage, relying entirely on the female for sustenance. He provides sperm for reproduction while the female continues her solitary life. This extreme form of sexual dimorphism and parasitism ensures that the anglerfish can reproduce in an environment where finding a mate is a rare occurrence.
Despite their fearsome appearance, anglerfish play a crucial role in the deep-sea ecosystem. As apex predators, they help regulate the populations of smaller fish and other organisms, maintaining the delicate balance of life in the deep ocean. However, like many deep-sea creatures, anglerfish face threats from human activities such as deep-sea trawling and climate change.
Deep-sea trawling can destroy the fragile habitats where anglerfish live, while climate change affects the availability of prey and the overall health of deep-sea ecosystems. Understanding and protecting these mysterious creatures is essential for preserving the biodiversity of the deep ocean.
The anglerfish is a testament to the incredible diversity and adaptability of life on Earth. From its bioluminescent lure to its extreme reproductive strategies, this deep-sea predator has evolved to survive in one of the most challenging environments imaginable. By studying and preserving the anglerfish and its habitat, we not only gain insight into the mysteries of the deep ocean but also ensure that these fascinating creatures continue to thrive in the darkness below.