Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
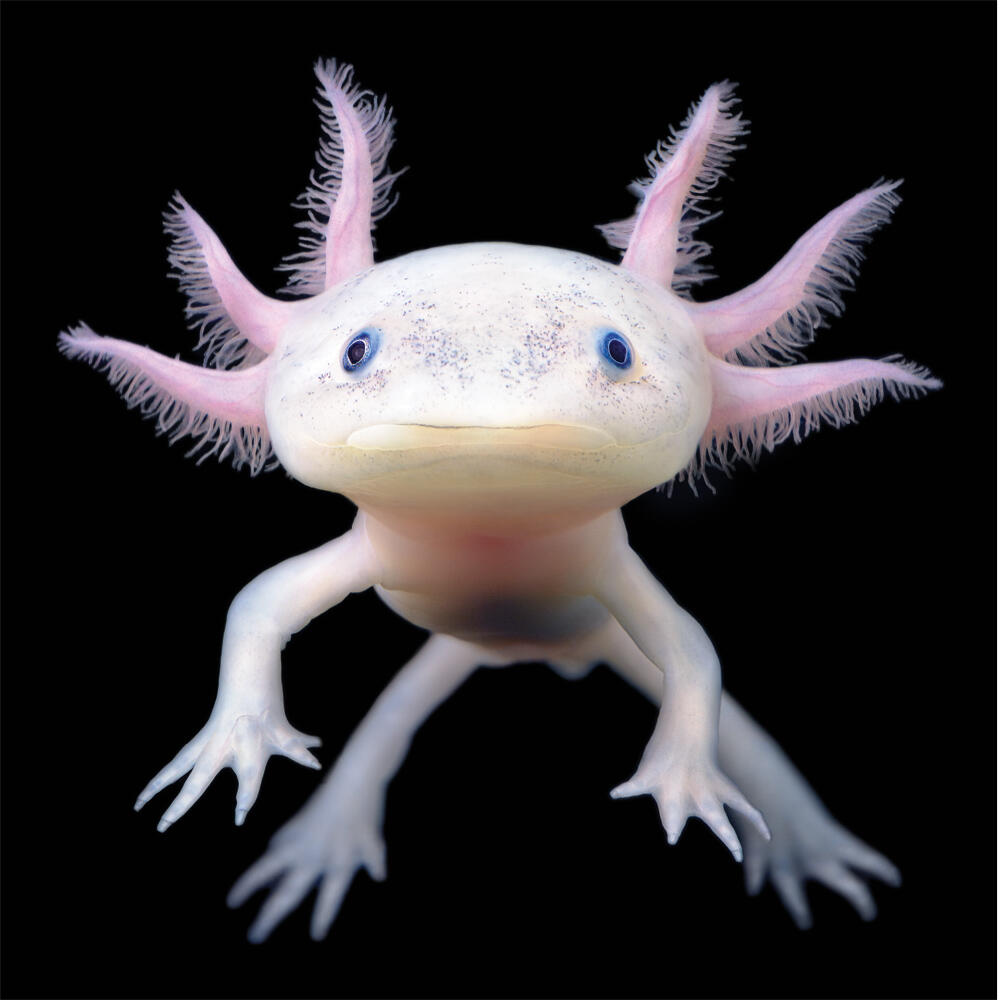

Imagine an animal that can regenerate its limbs, heart, brain, and even parts of its spinal cord. This isn’t a creature from science fiction; it’s the axolotl, a Mexican marvel that has fascinated scientists and animal lovers alike. In this article, we will explore the unique characteristics of axolotls, delve into their cultural significance, and uncover the latest scientific research that could one day revolutionize regenerative medicine.
Axolotls are known for their extraordinary regenerative abilities. Unlike most amphibians, axolotls remain in their larval stage throughout their lives, a condition known as neoteny. This means they retain their gills and aquatic lifestyle, never undergoing metamorphosis like their close relatives, the salamanders. This perpetual larval state is not just a quirky trait but a subject of intense scientific study, as it holds clues to their incredible regenerative capabilities.
Recent studies have shown that axolotls can regenerate complex body parts, including limbs, heart tissue, parts of the brain, and spinal cord. This regenerative ability is unparalleled in the animal kingdom and offers promising insights for human medicine. Researchers are particularly interested in understanding the genetic and molecular mechanisms behind this process, with the hope of applying this knowledge to regenerative therapies in humans.
Despite their popularity in research and as pets, axolotls are critically endangered in the wild. Native to the lakes and canals of Mexico City, their natural habitat has been severely reduced due to urbanization, pollution, and the introduction of invasive species. Efforts to conserve wild axolotl populations are ongoing, with various organizations and scientists working to protect their habitats and raise awareness about their plight.
One notable initiative is the Xochimilco Ecological Park, which aims to restore and maintain the natural habitat of axolotls. Additionally, captive breeding programs are being implemented to ensure the survival of this unique species.
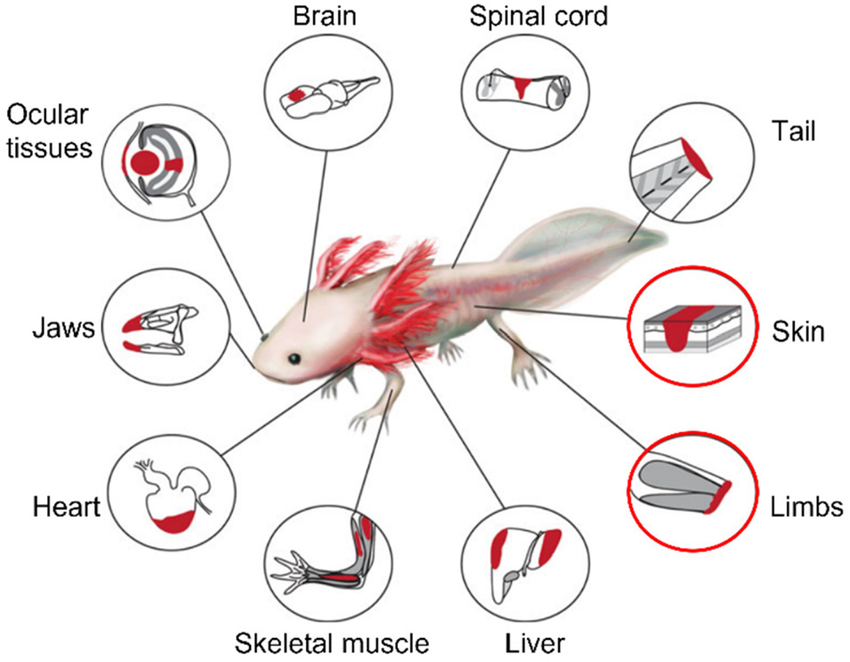
Tissue types the axolotl can regenerate as shown in red (Debuque and Godwin, 2016)
Axolotls have become a cornerstone in the field of regenerative medicine. Scientists at institutions like the University of Minnesota and Harvard University are unraveling the genetic codes that allow axolotls to regenerate their body parts. Recent breakthroughs include identifying specific genes and signaling pathways involved in tissue regeneration, which could have profound implications for healing human injuries and diseases.
One fascinating discovery is that axolotls can regenerate not just at the site of injury but also influence nearby cells to become regenerative. This cellular reprogramming is a key area of research, potentially leading to new treatments for conditions such as spinal cord injuries and heart disease.
To bring a personal touch to this scientific marvel, we spoke with Dr. Maria Ramirez, a leading axolotl researcher at the National Autonomous University of Mexico. Dr. Ramirez shared a heartwarming story of an axolotl named Xochi, who lost a limb to an infection but fully regenerated it within a few months.
"It's truly awe-inspiring to witness these creatures heal themselves," Dr. Ramirez said. "Xochi's journey is a testament to the resilience and mystery of axolotls."
Axolotls hold a special place in Mexican culture and mythology. They are named after the Aztec god Xolotl, the god of fire and lightning who, according to legend, transformed into an axolotl to escape being sacrificed. This cultural heritage adds a rich layer to the story of axolotls, intertwining mythology with modern science.
Historically, axolotls were also an important food source for the Aztecs and have been depicted in various artworks and literature throughout Mexican history. Their continued presence in the cultural fabric of Mexico highlights their enduring significance.
[Time-Lapse Video of Axolotl Limb Regeneration]
The axolotl is not just an extraordinary animal; it’s a symbol of resilience and hope in the face of environmental and scientific challenges. From their unique biological traits to their cultural significance and potential medical applications, axolotls continue to captivate and inspire. As we strive to protect these incredible creatures, we also unlock secrets that could one day transform human medicine, making the study of axolotls a journey worth undertaking.